ADVERTISEMENT
Pain or discomfort: Does your child complain of itching, burning, or tenderness?
Tip: Taking a photograph of the patch every day can help you track subtle changes and provide useful information to the doctor. Make sure the lighting is consistent, and include a reference (like a coin) for size comparison.
2. Possible Causes of Skin Changes on the Ear
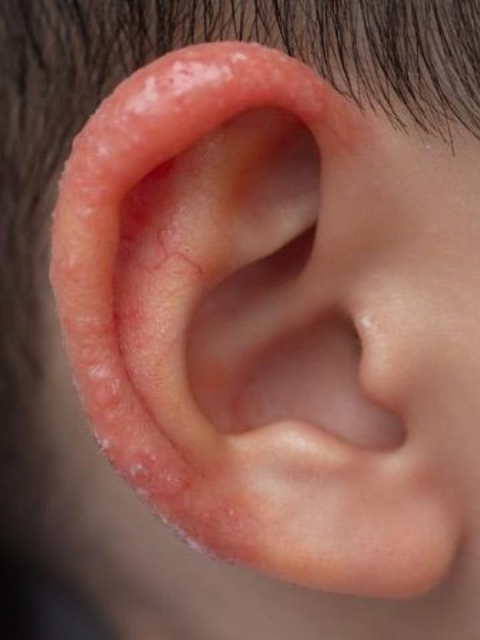
Several conditions could cause a new patch of skin on a child’s ear. While a professional evaluation is necessary for a definitive diagnosis, understanding possible causes can help guide temporary management.
Conditions such as impetigo often appear as red sores that may ooze or form yellow crusts.
Commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus bacteria.
Fungal Infections
Tinea (ringworm) may appear as a round, red, scaly patch that spreads slowly.
Molluscum contagiosum can appear as small, flesh-colored or pearly bumps.
Viral rashes (like those from chickenpox or measles) might involve the ear but often appear alongside systemic symptoms like fever.
Often presents as dry, itchy, or scaly patches.
Can occur on the ear, face, or behind the ears.
Contact Dermatitis
Typically red, itchy, and may blister or peel.
The distribution often corresponds to the area in contact with the allergen.
c. Skin Growths and Other Conditions
Birthmarks or Moles
Usually present from birth or early childhood.
Any rapid change in size, color, or shape warrants a medical review.
Continue reading…